Branchial Cyst

A branchial cyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops in the neck due to embryonic remnants. It can appear as a lump or cyst and may cause swelling, infection, or discomfort. Early diagnosis and surgical removal help prevent complications and recurrence.
Branchial Cyst
Branchial cyst is a developmental cyst that can appear anywhere in the neck. It can present as a lump, cyst or an abscess. These cyst can cause pressure symptoms, abscess formation , and has a potential for malignant transformation.
All cysts and lumps (in adults) in the neck require a fine needle aspiration which is a needle sample test of the lump. The aspiration is done with a very fine needle (smaller than blood sampling needle). The diagnosis is made by evaluating the aspirated sample by the pathologist and additional information from a CT or MRI scan.
These cyst should be excised with any associated extensions, tracts so this will reduce chance of recurrences. Surgery for these cysts can vary from 1 to 3 hours and 1 to 2 day hospital stay. Patients can resume normal activity within 5 to 7 days and the wound is well healed by 10 days.
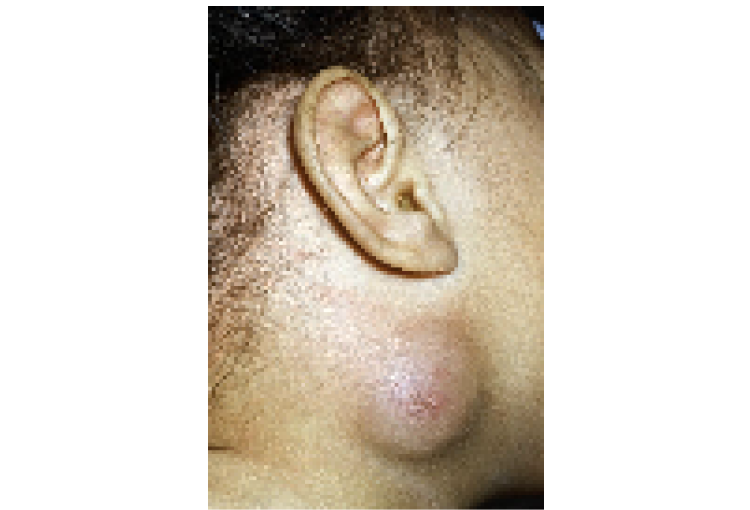
2 year old child with Branchial cyst - large 5 cm right neck
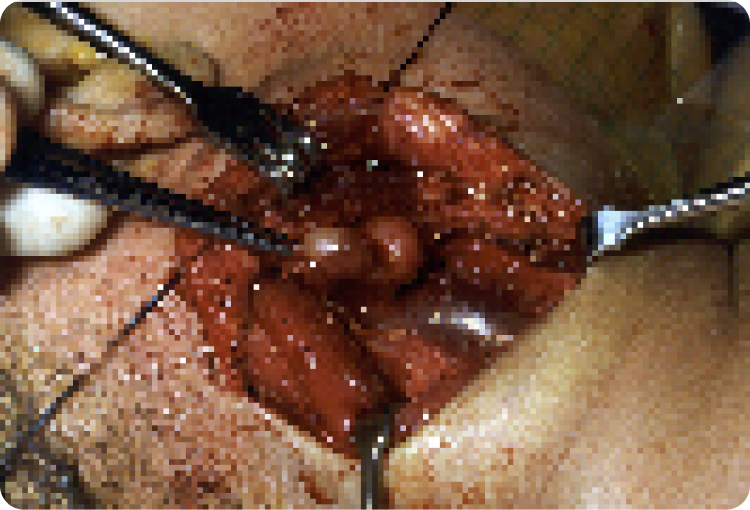
Surgical view of the cyst next to the jugular vein
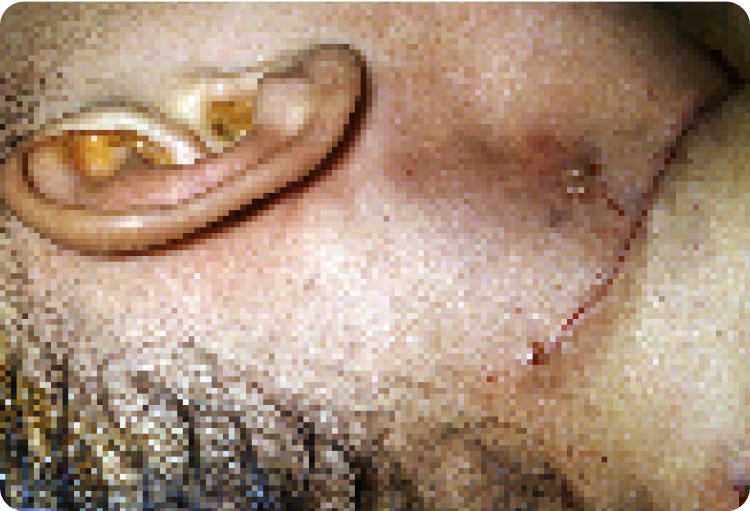
At the end of surgery
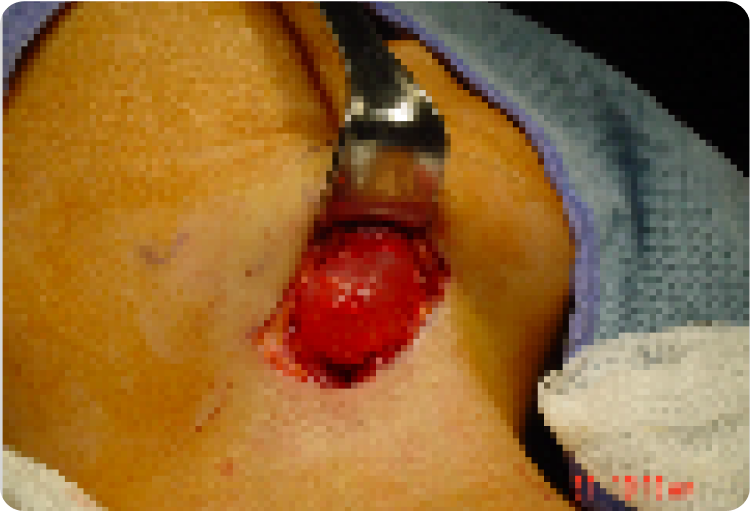
25 year old adult with Branchial Cyst in the right neck 4cm
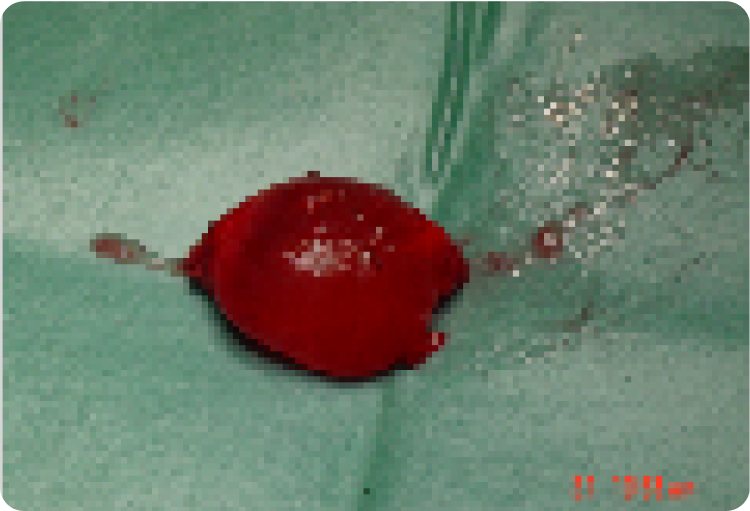

Removed cyst at end of procedure
Murali Mahadevan
Specialist ENT Surgeon
For all enquiries and appointments call (09) 925 4050
Suite A, Level 1, Kakariki Hospital
9 Marewa Road
Greenlane, Auckland 1051
Facsimile: (09) 925 4051
Only general information is provided on this web site and is not intended as advice or a consultation. Please read our full disclaimer.

If you're experiencing these symptoms, it's recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
FAQs
A branchial cyst forms from embryonic tissue remnants that fail to disappear during development.
While usually benign, it can become infected, form an abscess, or, in rare cases, undergo malignant transformation.
Diagnosis is done through physical examination, fine needle aspiration (FNA) for sample testing, and imaging like CT or MRI scans.
Surgical removal is the preferred treatment to prevent infection, complications, and recurrence.
Most patients resume normal activities within 5–7 days, with full healing in about 10 days.
If completely removed along with any associated tracts, recurrence is unlikely.
Contact Us
Get in touch to book an appointment or inquire about our ENT services. Our team is here to assist you with expert care and guidance.
Ph: +64 9 925 4050
Fax: +64 9 925 4051
Dr Murali Mahadevan FRACS
Otolaryngology Associates Ltd
Suite A, Level 1, Kakariki Hospital
9 Marewa Road
Greenlane, Auckland 1051

